As mentioned in the beginning of the previous page, we are now going to access array elements using a random number. We are going to set up a states and capitals program that gives the user a state and asks for the capital. The state will be stored in one dimension of the array, the correct answers (the capitals) in the next dimension, and the user's entry in the next dimension. This will becomes more clear shortly.
Open a new project.
Name the project Capitals.
Name the form frmCapitals.
Set the form's Height property to 3690 and the form's Width property to 4080.
Set the form's StartUpPosition property to 2-Center Screen.
Set the form's BorderStyle property to 1-Fixed Single and its MinButton property to True.
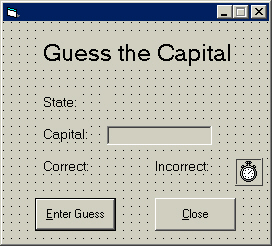
Set up the interface you see below:

Set the AutoSize properties of all the labels to True.
Name the top label lblTitle.
Set its font size to 18.
Name the label displaying State: as lblState.
Set the Index property of that label to 0.
Name the label to the right of lblState as lblState.
Name the label below displaying Capital: as lblCapital.
Name the text box txtState.
Name the next label down (the label displaying Correct) as lblCorrect.
Name the label to the right of that label (the label displaying Incorrect) as lblIncorrect.
Drag the mouse over the labels lblState(0) and lblState(1).
Set the font size to 10.
Select the remaining labels below and set their font size to 10.
Name the left command button cmdGuess and the right command button cmdClose.
Set the Default property of cmdGuess to True and the Enabled property to False.
Set their captions as seen and be sure to set the access keys.
Name the timer tmrTime.
Set the timer's Enabled property to True and its Interval property to 1000.
Once again, just be sure you set the AutoSize property of all the labels to True.
Lock the controls on the form.
Code the cmdClose command button to unload the form frmCaptials.
Select the txtCapital text box in the object box of the code window.
Press tab, then type the following lines:
If Len(txtCapital.Text) > 0 Then
cmdGuess.Enabled = True
Else: cmdGuess.Enabled = False
End If
I hope you understand this code by now.
Go to the General Declarations section of the code window and type the following lines:
Dim bytWrongGuess As Byte
Dim strCapitals(49, 2) As String
Dim intState As Integer, intTries As Integer
Dim bytMinutes As Byte, bytSeconds As Byte
Dim bytIncorrect As Byte, bytCorrect As Byte
Most of those variables should be self-explanatory as to what they will store. The variables bytMinutes and bytSeconds are going to store the total amount of time it takes the user to fill in all the capitals. The variable strCaptials is set up as an array 0 to 49 and 0 to 2. This stores the state, the capital, and the users guess.
Open the code window for the tmrTime object.
Press tab, then type the following lines:
bytSeconds = bytSeconds + 1
If bytSeconds = 60 Then
bytMinutes = bytMinutes + 1
bytSeconds = 0
End If
Obviously, this code begins in incrementing the variable bytSeconds by 1, then tests to see If the value of bytSeconds has reached 60 (which is one minute because the Interval of the timer is set to one second). When it reaches sixty, increment the variable bytMinutes by one, then reset bytSeconds to zero.
Now we will set up the array. Remember that we only want to store the state and the capital. The user's answer is written to the array during runtime.
Type the following lines in the code window for the form's Load event (maybe you should copy and paste the code below):
strCapitals(0, 0) = "Alabama"
strCapitals(1, 0) = "Alaska"
strCapitals(2, 0) = "Arizona"
strCapitals(3, 0) = "Arkansas"
strCapitals(4, 0) = "California"
strCapitals(5, 0) = "Colorado"
strCapitals(6, 0) = "Connecticut"
strCapitals(7, 0) = "Delaware"
strCapitals(8, 0) = "Florida"
strCapitals(9, 0) = "Georgia"
strCapitals(10, 0) = "Hawaii"
strCapitals(11, 0) = "Idaho"
strCapitals(12, 0) = "Illinois"
strCapitals(13, 0) = "Indiana"
strCapitals(14, 0) = "Iowa"
strCapitals(15, 0) = "Kansas"
strCapitals(16, 0) = "Kentucky"
strCapitals(17, 0) = "Louisiana"
strCapitals(18, 0) = "Maine"
strCapitals(19, 0) = "Maryland"
strCapitals(20, 0) = "Massachusetts"
strCapitals(21, 0) = "Michigan"
strCapitals(22, 0) = "Minnesota"
strCapitals(23, 0) = "Mississippi"
strCapitals(24, 0) = "Missouri"
strCapitals(25, 0) = "Montana"
strCapitals(26, 0) = "Nebraska"
strCapitals(27, 0) = "Nevada"
strCapitals(28, 0) = "New Hampshire"
strCapitals(29, 0) = "New Jersey"
strCapitals(30, 0) = "New Mexico"
strCapitals(31, 0) = "New York"
strCapitals(32, 0) = "North Carolina"
strCapitals(33, 0) = "North Dakota"
strCapitals(34, 0) = "Ohio"
strCapitals(35, 0) = "Oklahoma"
strCapitals(36, 0) = "Oregon"
strCapitals(37, 0) = "Pennsylvania"
strCapitals(38, 0) = "Rhode Island"
strCapitals(39, 0) = "South Carolina"
strCapitals(40, 0) = "South Dakota"
strCapitals(41, 0) = "Tennessee"
strCapitals(42, 0) = "Texas"
strCapitals(43, 0) = "Utah"
strCapitals(44, 0) = "Vermont"
strCapitals(45, 0) = "Virginia"
strCapitals(46, 0) = "Washington"
strCapitals(47, 0) = "West Virginia"
strCapitals(48, 0) = "Wisconsin"
strCapitals(49, 0) = "Wyoming"
strCapitals(0, 1) = "Montgomery"
strCapitals(1, 1) = "Juneau"
strCapitals(2, 1) = "Phoenix"
strCapitals(3, 1) = "Little Rock"
strCapitals(4, 1) = "Sacramento"
strCapitals(5, 1) = "Denver"
strCapitals(6, 1) = "Hartford"
strCapitals(7, 1) = "Dover"
strCapitals(8, 1) = "Tallahassee"
strCapitals(9, 1) = "Atlanta"
strCapitals(10, 1) = "Honolulu"
strCapitals(11, 1) = "Boise"
strCapitals(12, 1) = "Springfield"
strCapitals(13, 1) = "Indianapolis"
strCapitals(14, 1) = "Des Moines"
strCapitals(15, 1) = "Topeka"
strCapitals(16, 1) = "Frankfort"
strCapitals(17, 1) = "Baton Rough"
strCapitals(18, 1) = "Augusta"
strCapitals(19, 1) = "Annapolis"
strCapitals(20, 1) = "Boston"
strCapitals(21, 1) = "Lansing"
strCapitals(22, 1) = "St. Paul"
strCapitals(23, 1) = "Jackson"
strCapitals(24, 1) = "Jefferson City"
strCapitals(25, 1) = "Helena"
strCapitals(26, 1) = "Lincoln"
strCapitals(27, 1) = "Carson City"
strCapitals(28, 1) = "Concord"
strCapitals(29, 1) = "Trenton"
strCapitals(30, 1) = "Santa Fe"
strCapitals(31, 1) = "Albany"
strCapitals(32, 1) = "Raleigh"
strCapitals(33, 1) = "Bismarck"
strCapitals(34, 1) = "Columbus"
strCapitals(35, 1) = "Oklahoma City"
strCapitals(36, 1) = "Salem"
strCapitals(37, 1) = "Harrisburg"
strCapitals(38, 1) = "Providence"
strCapitals(39, 1) = "Columbia"
strCapitals(40, 1) = "Pierre"
strCapitals(41, 1) = "Nashville"
strCapitals(42, 1) = "Austin"
strCapitals(43, 1) = "Salt Lake City"
strCapitals(44, 1) = "Montpelier"
strCapitals(45, 1) = "Richmond"
strCapitals(46, 1) = "Olympia"
strCapitals(47, 1) = "Charleston"
strCapitals(48, 1) = "Madison"
strCapitals(49, 1) = "Cheyenne"
As you see in the array, we store the state in array dimension 0. The first number is just the state number (not the actual number that the state has in the US, but the index of that element in the array). The states are stored 0 through 49, which is fifty total elements, just as there are fifty total states in the US. The capital is stored the same way, but in array dimension 1. If this is difficult to picture see below.
The array looks like this:
| State | Capital | User Entry |
| Alabama | Montgomery | |
| Alaska | Juneau | |
| Arizona | Phoenix | |
| Arkansas | Little Rock | |
| California | Sacramento |
And so forth.
Go to the top of the code window.
Press enter twice at the end of the last in the General Declarations section.
Type the following lines:
Private Function State()
intState = Int(Rnd * 50)
lblState(1).Caption = strCapitals(intState, 0)
End Function
Line 1: Begin function called State.
Line 2: Set the variable intState equal to a random
number times
fifty (which includes values 0 through 49), then
convert the
result to an integer.
Line 3: Set the caption of the label lblState(1) to the
text in
the array strCapitals with the value of intState,
looking in
dimension zero.
Line 4: End the function.
Go back to the form's Load event procedure.
Above the lines already there, type the following lines:
Randomize
intState = Int(Rnd * 50)
intTries = 0
bytCorrect = 0
bytIncorrect = 0
bytMinutes = 0
bytSeconds = 0
Line 1: Initialize the random number generator.
Line 2: Generate a random number from 0 to 49
and store the
number in the variable intState.
Lines 3 through 7 set the variables listed to zero to
give them a
base value.
Create a blank line at the bottom of this procedure, then type the following lines:
lblState(1).Caption = strCapitals(intState, 0)
lblCorrect.Caption = "Correct: " & bytCorrect
lblIncorrect.Caption = "Incorrect: " & bytIncorrect
Line 1: Set the caption of the label lblState(1)
to the text in the string array dimension with the value of intState,
looking in part 0 (dimension zero).
Line 2: Set the caption of the label lblCorrect to
"Correct:
" and the value of the variable bytCorrect, which is zero when
the
form loads.
Line 3: Set the caption of the label lblIncorrect to
"Incorrect: " and the value of the variable bytIncorrect, which
is zero when the form loads.
Now we are going to finish this application off by coding the cmdGuess command button. Be ready to type a whole lot more code!
Open the code window for the command button cmdGuess.
Press tab, then type the following lines:
Const conBtns As Integer = vbYesNo
Dim intResponse As Integer
Dim bytDimension As Byte
strCapitals(intState, 2) = txtCapital.Text
intTries = intTries + 1
Line 1: Declare constant conBtns as an Integer
to store a Yes and No button, which we will use to
prompt the user
later.
Line 2: Declare variable intResponse as an Integer
to store
the user's selection in the message box.
Line 3: Declare variable bytDimension as a Byte
to look in
the array elements.
Line 4: Set the strCapitals array dimension 2,
looking at
the part with the same value of the variable intState to the
text in the txtCapital
text box.
Line 5: Increment the variable intTries by one.
Below the lines you just entered, type the following lines:
If strCapitals(intState, 1) =
strCapitals(intState, 2) Then
bytCorrect = bytCorrect + 1
bytWrongGuess = 0
lblCorrect.Caption = "Correct: " & bytCorrect
Call State
Line 1: Test to see if the strCapitals
array
element 1 (the capital of the state) and array element 2
(the
user's guess) are equal AND check to make sure the value of intState
is
less than 50.
Line 2: When all of the above is True (basically, the
guess is the
capital), add one to bytCorrect.
Line 3: Reset the variable bytWrongGuess.
Line 4: Set the caption of the label lblCorrect to "Correct:
" (which resets the label) and the value of the variable bytCorrect.
Line 5: Call the function State to get a new random
number to set
in place for one of the array elements.
Below the code you just entered, type the following lines (be sure you type it STILL within the If statement above):
Do Until Len(strCapitals(intState, 2)) = 0
If intTries < 50 Then Call State Else GoTo Finish
Loop
Line 1: Begin Do Until loop --> it
will execute
the loop statements (the next line) until the Length element 2
of
array strCapitals looking at the dimension value of intState
is
equal to zero, or when there is no text in that dimension.
Line 2: Test to make sure that the value of the variable intTries
is less than 50. When intTries is less than 50,
call the
function State, which generates the random number then looks in
the array
dimension according to that value (if the value is 15, it looks in
array
dimension 15, and so forth). It keeps calling the function
until the
array element corresponding with the value of intState is
blank, which
means the user has not yet entered text into that element.
Line 3: Make the Do Until loop loop. Tell the
loop to keep
looking in the array Until there is no text in that dimension
(which line
1 does).
Press enter, then press backspace.
Type Else (tell the procedure to do the following when the user enters the wrong capital).
Press enter.
Press tab, then type the following lines:
intTries = intTries - 1
bytIncorrect = bytIncorrect + 1
lblIncorrect.Caption = "Incorrect: " & bytIncorrect
bytWrongGuess = bytWrongGuess + 1
If bytWrongGuess = 2 Then
MsgBox "The capital of " & strCapitals(intState,
0) & " is " & strCapitals(intState, 1) & "."
bytWrongGuess = 1
bytIncorrect = bytIncorrect - 1
lblIncorrect.Caption = "Incorrect: " &
bytIncorrect
End If
Line 1: Decrement intTries by one
(subtract one).
Line 2: Add one to the variable bytIncorrect.
Line 3: Set the caption of the label lblIncorrect to
"Incorrect: " and the value of bytIncorrect.
Line 4: Increment the variable bytWrongGuess by one.
Line 5: Test the value of the variable bytWrongGuess;
when it is 2,
execute statements on lines 6 through 9.
Line 6: Display a message box telling the user the capital of
the state
currently displayed in the label (the state in array element strCapitals(intState,
0). Basically, if the user has already typed in a capital wrongly,
this
prevents them from entering the capital in for the same state again
wrongly.
Then we tell them in the message box.
Line 7: Set the variable bytWrongGuess to 1.
Line 8: Subtract one from the variable bytIncorrect so
that the
user does not keep incrementing their wrong answers.
Line 9: Set the caption of the label lblIncorrect to
"Incorrect: " (to reset it to normal) and the value of bytIncorrect.
Press Enter then Backspace.
Type End If.
Press Enter.
This ends the first If statement in the sub-procedure. It was a very LONG If statement as you see.
Type the following lines:
txtCapital.SelStart = 0
txtCapital.SelLength = Len(txtCapital.Text)
Exit Sub
Press Enter.
Line 1: Set the selection start (SelStart)
of the
text box txtCapital to zero, thus moving the cursor all the way
to the
left of the text box.
Line 2: Set the selection length (SelLength) of the text
box to
the length (Len) of the text in txtCapital, thus
selecting the
entire string (the existing text).
Line 3: Exit the sub-procedure. We will soon enter code that we
do not
want the sub-procedure to execute (recall the Goto Finish line
earlier).
Type the following lines below the code you just entered:
Finish:
intResponse = MsgBox("You have finished! You entered " & bytCorrect
- bytIncorrect & _
" capitals correctly in " & bytMinutes & " minutes and " &
bytSeconds _
& " seconds. Would you like to try again?", conBtns, "Capitals")
If intResponse = vbYes Then
For bytDimension = 0 To 49
strCapitals(bytDimension, 2)
= ""
Next bytDimension
intTries = 0
bytMinutes = 0
bytSeconds = 0
bytCorrect = 0
bytIncorrect = 0
lblCorrect.Caption = "Correct: " & bytCorrect
lblIncorrect.Caption = "Incorrect: " &
bytIncorrect
Call State
Else
Unload frmCapitals
End If
Line 1: Set the label Finish for the code we entered
earlier to
Goto.
Line 2: Display a message box telling the user how many capitals
they
answered correctly (bytCorrect - bytIncorrect), how many minutes
it took
them, and how many seconds it took them. Then ask them if they would
like to try
again, and store their response in the variable intResponse.
The
underscore treats the line beneath it as part of its own line. Since
this is a
rather long line of code, it looks much better to enter code on
multiple lines.
Lines 3 and 4 continue the message box.
Line 5: Test to see what button the user pressed in the message
box. When
they press Yes, execute lines 6 through 17.
Line 6: Look at values 0 to 49 for dimension 2
of
the array strCapitals by way of the variable bytDimension.
Line 7: Clear elements 0 through 49 (values from
line 1) of
dimension 2 in the array strCapitals, thus clearing all
of the
user's answers.
Lines 9 through 13 reset the listed variables to zero
(their
initial state).
Line 14: Set the caption of the label lblCorrect to Correct:
(which resets the label) and the value of bytCorrect (now set
to zero).
Line 15: Same as line 14, but with the label lblIncorrect
and the
variable bytIncorrect.
Line 16: Call the function State in order to find
another state at
random.
Line 18: Otherwise (user does not want to try again), unload the
form.
Well done getting through this tutorial. I hope that you made it through error-free!
Now you may proceed to Page 28.